Hello everyone! In today’s post, I’ll be solving a challenge from Daily AlpacaHack. I’m still not very confident in cryptography, so I’m using this challenge as a way to learn and understand it better. Let’s walk through it step-by-step and figure it out together!
Description
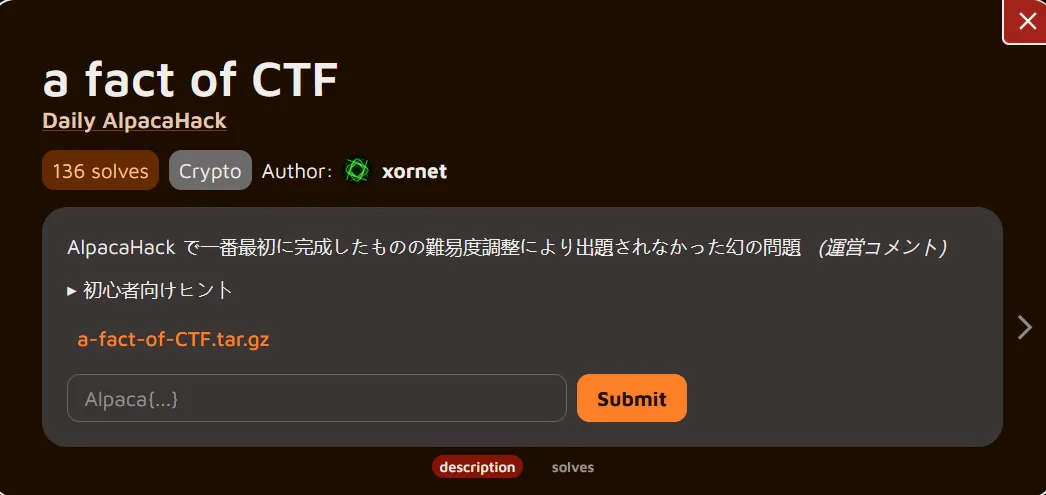
Translation :
The phantom problem that was never released due to difficulty adjustments on AlpacaHack's very first completed challenge (Organizer's note)Hint for beginners
This problem belongs to the Crypto category, meaning it's about cryptography. AlpacaHack currently focuses on four main categories: Crypto, Pwn, Rev, and Web. Other problems are classified under the Misc category. First, download and extract the attached file a-fact-of-CTF.tar.gz. The script chall.py reads an environment variable named FLAG. This is the flag. It then transforms this flag using prime numbers. The output from this chall.py script is saved in output.txt. The goal of this problem is to reverse-engineer the flag from the values in output.txt.Understanding the challenge
This is a cryptography challenge where we’re given an attached file containing two components: the script chall.py and an output.txt file. The Python script reads an environment variable named FLAG, encrypts it using prime numbers, and stores the encrypted result in output.txt. Our goal is simple: reverse the encryption process and recover the original flag from the value inside output.txt.
Solution
First, we download the provided file:
┌──(chjwoo㉿hackbox)-[~/…/ctfs/alpacahack/cry/a-fact-of-ctf]└─$ wget https://alpacahack-prod.s3.ap-northeast-1.amazonaws.com/1703ffac-8c0c-4a2a-a8ff-bb11a932ed56/a-fact-of-CTF.tar.gz--2025-12-02 14:31:20-- https://alpacahack-prod.s3.ap-northeast-1.amazonaws.com/1703ffac-8c0c-4a2a-a8ff-bb11a932ed56/a-fact-of-CTF.tar.gzResolving alpacahack-prod.s3.ap-northeast-1.amazonaws.com (alpacahack-prod.s3.ap-northeast-1.amazonaws.com)... 3.5.159.119, 52.219.136.178, 52.219.199.74, ...Connecting to alpacahack-prod.s3.ap-northeast-1.amazonaws.com (alpacahack-prod.s3.ap-northeast-1.amazonaws.com)|3.5.159.119|:443... connected.HTTP request sent, awaiting response... 200 OKLength: 4701 (4.6K) [binary/octet-stream]Saving to: ‘a-fact-of-CTF.tar.gz’
a-fact-of-CTF.tar.gz 100%[=======================================>] 4.59K --.-KB/s in 0s
2025-12-02 14:31:20 (232 MB/s) - ‘a-fact-of-CTF.tar.gz’ saved [4701/4701]
┌──(chjwoo㉿hackbox)-[~/…/ctfs/alpacahack/cry/a-fact-of-ctf]└─$ lsa-fact-of-CTF.tar.gzExtract the archive:
┌──(chjwoo㉿hackbox)-[~/…/ctfs/alpacahack/cry/a-fact-of-ctf]└─$ tar -zxvf a-fact-of-CTF.tar.gza-fact-of-CTF/a-fact-of-CTF/chall.pya-fact-of-CTF/output.txtAnalyzing the code
Now let’s break down what the script is doing:
import os
flag = os.environ.get("FLAG", "not_a_flag")
# all prime numbers less than 300primes = [2, 3, 5, 7, 11, 13, 17, 19, 23, 29, 31, 37, 41, 43, 47, 53, 59, 61, 67, 71, 73, 79, 83, 89, 97, 101, 103, 107, 109, 113, 127, 131, 137, 139, 149, 151, 157, 163, 167, 173, 179, 181, 191, 193, 197, 199, 211, 223, 227, 229, 233, 239, 241, 251, 257, 263, 269, 271, 277, 281, 283, 293]assert len(flag) <= len(primes)
ct = 1for i, c in enumerate(flag): ct *= primes[i] ** (ord(c))
print(hex(ct))Here’s how the encryption works:
- The flag comes from the environment variable
FLAG. If it’s missing, the script defaults to"not_a_flag". - It defines a list of all prime numbers less than 300.
- The flag length must not exceed the number of primes (62 characters).
- The ciphertext
ctstarts at 1. - For each character:
- Take the i-th prime number.
- Raise it to the power of ASCII value of the character.
- Multiply that into the ciphertext.
This is a classic prime encoding scheme. Because prime factorizations are unique, we can reverse it by factoring the ciphertext and mapping each exponent back to a character—essentially reversing the encryption.
Solver
ct = 0xadb88e47d531cdb104013d7aa8a21e6f5bfb841d2ff5d5090d735f9a1d9f6bb2dc0ad6d19efca47ec943e5a8b685f295be56d3531fcb49e41d5d02dd6113e3fcd369a5c25098b38e540fc865e2f1078292efc89778b5f29e74b188c87afcdeb9f4c58d77d1314271646bc1043c63e62b76396f1349b914a0d489df9c211c6e551969694c1a930f8e04379a589869c4a838d0db71168f61b8ff38c6107fca44d2b5064ed42a4b8bbd774025f43907275317679daa0fb58e4127eac72eedb6be263fc0897f6d791eb3b301321b1e0ed37234b92249fe164f5b1a85981e7b52d65e50315520bfcf9c45f86e6d9c899e7aaefa936fa1a7f14dbb9bc9d9615dc9d97e7aecf162549866488b99d6903586f0cbdabfa0de664e66b8e36dadc2fec12d09a6ac3d33b6cdd8aaeccf58f7a3abbc2bcce34652f08617b33583568a1c5335a13d1530c69284d13df513314aa5b12db052529faf61461107d088008658730bce9af8ac9a9b262df3f1e9c84334f3616e9ed9d6598c4a70e9894b47ad73b415713371a5ced21f2853e02f0cce55969ff3101fb9da00c6f48932fa8696ee474bee89d462e08038566ea125f56733f029f40d13ea98a92ddbfcd7b0c900e8b1c7bc65124ae620279e7ae00fb8ef65f835665e344d570325330f90c85326571fd96ba2883fc7b2b6615f35d555948acf3c0ae684a0af323011d209dd8374649dec9bbdaa0ab7068af63fdaacbc5177fd75b457e91fec461a33a0fcb55754d655f2fb9e198d81df64009e9e1e34bddb349955d0792d9717161ba4538b564d85fb6630e2acb4bc95130f6c9d31d6f53aeaecd4c023c50df0b8e2e50c84db4051261abaf38f7020b2964ba6ad05932e22428ae773e78dc83014e674261859b65bd7c9d4b328dd9abbae1067f735006d4400f8c595ee01904fcbdf54c34f983826c24876877f76b9ee14327ddb6b7a7a2625a65a92c2ea757f42d0a3a6fb824d00c9ad4fb4cb2b2c77b0d66b89fc4846b5448df3bfa8977a8e42e9ea4ec5948264f0cd8efeec387c0344b56017657679605b1d0bc32fb1742b1cb8f2426e35e1e673c6af6ae5f3d3bda56b4de192f994f3aef809ae92dda1ab20aef0a948c9bdfecb896727856a0d8a0d9af81661ba53c7927223b2389a168c8adc04f1e7a07499d308bf9cdbe55220a5fa392879d644f3c25949c7d4d6aee482525ad22c3bde07e16fcc1788362bf365c0e12db42e0ad2ce29d666bed43f24dadfec45008b6c1dd96649c2afbbd392e635b5185fe5c8f9374eb6c7418cd5c4400a8025eb989e1ca66943e02e7d54b2744c51e17de2a919972c7deac0735501ce812b9453e2e14d22ec1dd2e87af06d47e8118c27a6357e006d774f053f977619347b62c6f01bf810369924295c4e097a6e8586eef1e310e787d870b0c4bee2e0d0a63b1dde4ef656213788dad7214e61d76c5b850c13836fc35ce85840ca5c450459753295ed628af60fb102c26208ac7bd09f5b02f9b4800eb486e41e4bfe780e02993a3259a5e310b404069bc15d2230b26a7f5e3d53df96ece4d51086444cb5bd24fb507f31869b248facccff49d5cf43643013f144af758c41405a02fd70564bea480b3a157059c1fab45e89bfd7caf543e2605d0d7e06ddb343cf2d03377355a12d818b430b8614687834a37bb0442197d9803fdab84129c864708031959b99abebbe013c221f5397d25750a9b8fd7d004a017646f0792c87ade48e6138bd554fdb2df57b980bdb073c805f99754affbcca377a37c9383c68add373c879ab309efc144234a1b55b44012bc5fad42e2b9c7ca13421cffb68b3dbfe6d5b6d009e02ae27bd45203c1db0bf250c22ffbc689f21b8b503ca5091465ef28295e307084cffb00f3af88bb0ffecaaa10496c866aceedd97059731b6defc3501b399ad7b8ff57f66872ad49573df06aeffe097ae904914d78991ba6008de217fb7f766044ab7a1fd79878f87df9fb3ad74024bfadc4a3a781216b141e2ac6c34ce76f0cf60a33a0c44a9a31770c279e7b11b87380de18406b5cd7c4892cb49ff5a8ef07c95a4c669eff91f424308342f68bb558c240c8a66393a561d659ada61b0fd595a155bca28054b13fe3aef57ba3fff5a39c92c0f4b8c5e3f8ef8aaa27aef70c1a065d10c107f2354f117b7f00db658326e07b8c3c6c833a3742a98a99e40ec978b71c656612da7c232575685e0f00c4fa51c0f13d064798b82db23a192bb6b8db0319fc3924929b350fbef650395d408df85e6fc5b63294ea8f36f98473f5a4b273e1a0a4b9545512547e8aabe1381989b6e241d47fd121f51478829a6557ab83bfa3579940c2d08201b24b09d209928f3914672ae60d1be1aa1dd20d7908d68da91c49523109a64bc553b4d89aa704f1628c9cca45b2ad157a874eb3afbd7d5e34bc958bf46bd455b2899a3033743af16d467eda2fd0c9b7f8892a82a8763c41c1fb112f2ecad17ae30da44db3d8f8a9a61510354fc5e072fe12b556f98edb933c9319e232451fa422d7cfed27af993fdd40913c6ddbfe9a89f1ae37c7ee8c2b058870daa04127f56ad5acafdb6accfd9fe66b49d653a39ccecf3dbade95b7eea178fdc82a7e6e5e3f118c9b800f96ab85a9109379dbf56a84ffe6fad6fc3bda0bc9968e231d34aacd5bb8c7f72630ca9cba7d7764c8abe5aa545cf9975dc163302ceee56865e4306accc9011e80134378f131fb6255c8af6d2d94d5f3e73b3c0cd2c6a86fd97e016641ea05bb61f97d701e413ecc376c07395fa5b7d615c6a32cc3fd3cad5669c925bedacf102f1f611f82a157a7362c01c095432c13e75707605e07d39d6caaa1693b06e266fbeb29be640125361071fa98c6e9c236c12ca5d0c88ad45ab8e2d6d2962ea454c30572d6347b13670d4ee9f75e1c17a71edd79fbd0c58ff3ba2eec6a5cd017187fb85cb396490012155ec40a2f002a38dca1396affafd43b6fa28f54e42eaef83982f4050b8c70b6091e07a08ac8d5b74bd7cd2fc86014e174e8d1f53cfd9277858ed4e16833daf3fb4902b8b782d7bab0cdabcfa6c0d922baf5cefa7bc110434a474d9de2c3312ddd7cf457a837cd762d2f3444054ff7389d81bc52a6bdb9731bd34a77f48bc8fc383f1bdd46ef5666df0d2f41ba359c8168ae5bd0d5ec36a85b9ec5a1469af81ef4f5254fb4b0e7d31c64ea4fc9975f157872b7f178d792877be60a014622a7594746017fea2e8c50926a36c0294249cd2d1b3ffb060eaa8050b906f4adb6acbf8446e9b22256d3e32dc63dbde922f0296b66d57c32f4d8ad5382d3159f787e4474f48a5d1033ba4760b9f74b66751efc7375b48c55ab3817458ca71ac52b8360da2f512f247e4b99fea2a43f423fcd76bfb9e64a2a0fcd69a3876c517ecaab5a4efffa8e957ba647eea810953e1554345872488a7b7b60735689c20e3ac9d5345c935bfaf80c3a6fafd1cd551457e3f8c4caa24568443b5afd0bd6eeda07938838bcb946460c9e882b3af29ca787b7a0b03ac3318cd720f7b08169096aee70c26bb59f3fcb39fef1d02140f43c4e6ba06e8eaf87f20685962fbbf1609216be320168e05b3ea734687779e8453ee4b44e793ccce8a541ec26781d980a58ec6625f194b7485bfd980f61ddcdc18626cc60b7754951520256f1676a35b64ee4d3f46c8a992fd824a425019b90c5ceb90c5feec0d3ba970f46cb5736f8e2673fabc8b40ea71730ca6e7dc45efff9126528f3e8c976ae1c1c2a9ed1f09fc848e986a8e2a771865424a16f8f3f8fd86e5c9c7bec7f7f698ddcd45b33f7b82b2973b075e46b07d415f50a845eb214d49f975b03c471fa4f8bd3c73261c4037eed7815f388c4e454737cff44fa12d358336ad5f0f8df8da4ba572a0e71012bcb776c41ea29bbab45c2645c880d4108f1de20a867464513414d5aeab3621a2cc08ce9370a2d64a0dbc0aff5f0722cdabfc3d90dfc2ac63b65f4a6e9111ae0595b1c03e7d55d16449d6f8b1ae6328cd3b29189ed9eb34ad5b1541f8596f302d0254c32ee04a555d1ba9567c47fafdfdb05b98783e04d2052d4594f8c7549b048c11477229228e3be8cdb214218e9069a2f21ed370b12df6708357db5b3e8dbf1895ea167c77ec4b6beb93fa7d6fb61737b61beffadf5f3b533be8730caec2ef1fe47bbee3d204ae007bd2c0b7a1c1784a71e0d85d6317111079a5d4e74c62304f6c91ba32b8e5f62ac68811cc0d67d9707173129c5ce874d6d52c1178b6eb86a739df6c27020ebb489224f1d5ca08ada416f5dad9f224a795b475ceca4fedceef605e96c5cb939ec6c361463bc86bdfc6c5c5f24b42888b59e229082b024f78eb28b9190beb46a2802dfef1f9019511118cd8dd338b1e3ac04235cb6a31afb49b27fee71da3a387a1904acd74799ce5211e3c2c43b66ad6a050b70b28a2dac3294abc1d53cb9df334546ef70f7aa29e93a0902fd23b0a554570e0271a49b8c548b5cf846c04f80dd922749b53f4f0db901e4c97c1209236adf891e184564a6b94f3da00e2fb548fb581c204eec117f8381a735f2fcecfd69c31d15342b053d5681fc97644c51e604f99299c7679727b25f73d863f83e0bc2288255af7c0720bd3b0f1820e60895a0d37f60ee05b928f7311f97434dd527fc2f4a33c8d0f4e4e3f7e160afa1a2731c522eef280702dd4eba358370cd6c9386c196d351f2ef8935045efb196d6b6a11e42209f0a4b64f4aea7b830ee131bd46d33d36f42dcfe833e5fddf59ea417c5ddb8a80c50957e3eec9177277483d1231d0e5f40aea3bfa9eec670bf19a72e0b96a3f9be8a8c63cca7960c374d2196881aafef24d32b2d582bd562dfd8d1996f1e7f73e412e3690ae5a492e11d173f04ba9e68d8d9cfaaf322eec828f95be3fe7e4c8dfc156993edb40321d40fb59cba71775581b2186fdd0271c04d85373e1022be81e21998a360bc1ba46dfd69bfb4dbedf43f9688483cab2002de982ec8e9ced314aac88b37694fcb63a41b7f245425c0455c146dfad31cd56174e92fcc6eb7e0000000000000000
primes = [2, 3, 5, 7, 11, 13, 17, 19, 23, 29, 31, 37, 41, 43, 47, 53, 59, 61, 67, 71, 73, 79, 83, 89, 97, 101, 103, 107, 109, 113, 127, 131, 137, 139, 149, 151, 157, 163, 167, 173, 179, 181, 191, 193, 197, 199, 211, 223, 227, 229, 233, 239, 241, 251, 257, 263, 269, 271, 277, 281, 283, 293]
flag = ""
for prime in primes: count = 0 while ct % prime == 0: ct //= prime count += 1 if count == 0: break flag += chr(count)
print(f"Flag: {flag}")What we do:
- The encrypted flag is provided in hexadecimal format. It represents a very large integer produced by multiplying prime numbers raised to the ASCII values of each character in the flag.
- To decrypt it, we must use the exact same list of prime numbers that were used during encryption (62 primes in total).
- The decryption process works by reversing the prime-exponent multiplication through prime factorization. We start with an empty flag string and iterate through the primes in the same order they were originally used.
- For each prime, we repeatedly check whether it divides the ciphertext. This is done using a
whileloop that keeps dividing the ciphertext (ct) by the current prime using floor division (ct //=), as long as the remainder is zero. - Each successful division increases a counter. This counter represents the exponent of that prime—exactly the ASCII value of the original character.
- When the loop finishes for a given prime (meaning
ctis no longer divisible by it), we check the value ofcount. - If
countis zero, it means there are no more characters to extract and the flag has been fully recovered, so the loop is terminated. - Otherwise, the counter is converted back to a character using
chr(count), and that character is appended to the reconstructed flag string. - This process repeats for each prime in the list until we rebuild the entire flag.
In the end, the decrypted flag is printed.
This works because the encryption process used unique prime factorization, making each prime’s exponent correspond exactly to one character in the flag. Since every integer has a unique factorization into primes, reversing the encryption is straightforward once we know the prime list.
┌──(chjwoo㉿hackbox)-[~/…/alpacahack/cry/a-fact-of-ctf/a-fact-of-CTF]└─$ python solver.pyFlag: Alpaca{prime_factorization_solves_everything}Flag
Alpaca{prime_factorization_solves_everything}